Marine Animals Definition Biology

It is the largest and most diverse biome in the world.
Marine animals definition biology. Marine biology is the study of plants and animals that live in saltwater therefore a marine biologist is someone employed in that field of study. Name the three body forms of sponges and define. Earth is often referred to as the blue planet because seas and oceans cover more than 75 of the Earths surface.
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life organisms in the sea. Marine biology the science that deals with animals and plants that live in the sea. It also deals with airborne and terrestrial organisms that depend directly upon bodies of salt water for food and other necessities of life.
But marine biology is so much more than making a dolphin -- or sea lion -- follow commands. The study of this biome and its components is known as marine biology while the scientists who study marine life are known as marine biologists. Marine biology is the study of marine organisms their behaviors and interactions with the environment.
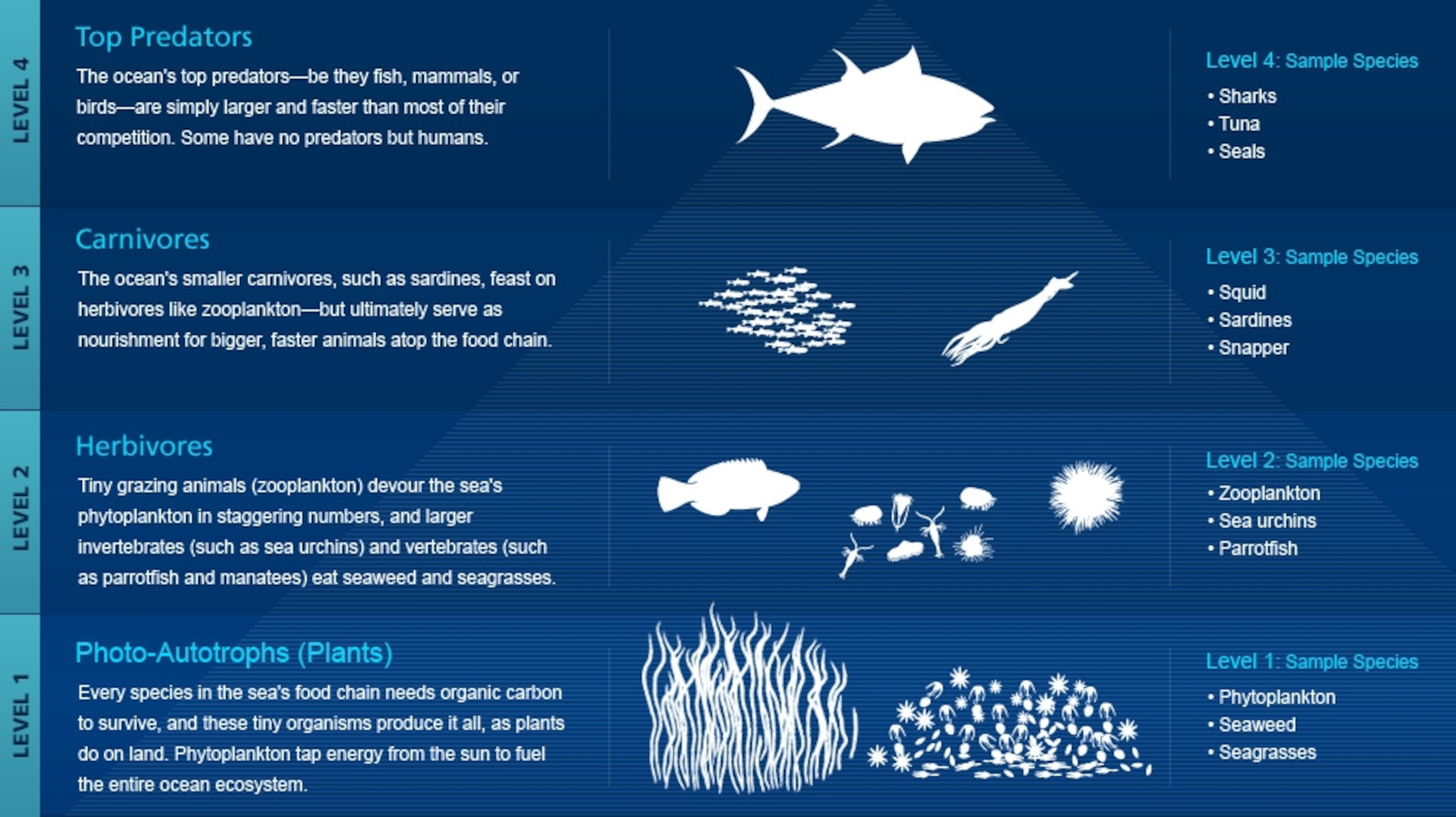
Marine biology is the study of animals that live in the oceans or other marine water bodies. In this context the word marine is interchangeable with saltwater. So a marine biologist studies.
Spongin- flexible protein fibers. Spicules- skeletal elements that support a sponge. The study of marine life is called marine biology and a person that studies marine life is called a marine biologist.
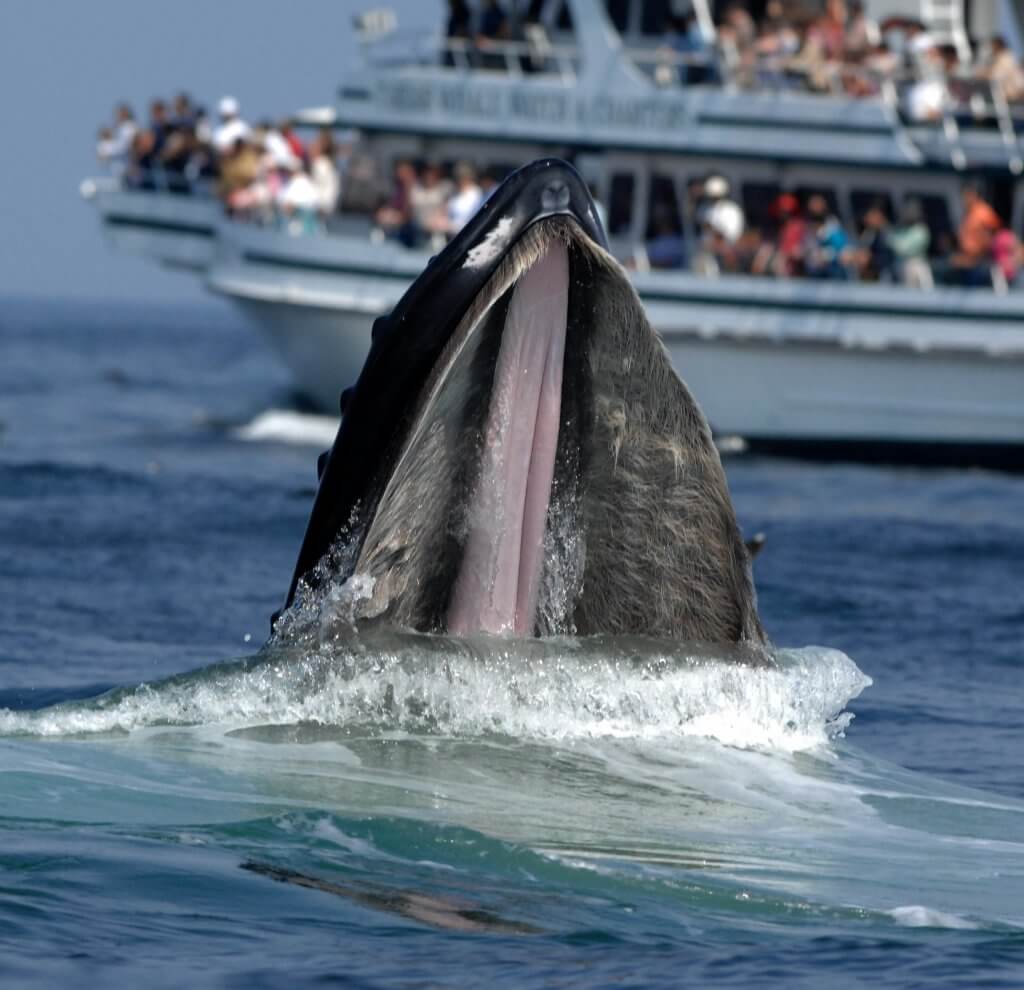
Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge. A thin colorless transparent oil that forms a waxy material when it comes into contact with air. Marine biologists study a wide variety of aquatic organisms from microscopic plankton to massive whales.