Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Where cellular respiration happens.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell.
The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Cellular respiration biology definition.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose. During cellular respiration glucose in the presence of oxygen is converted into carbon dioxide and water.
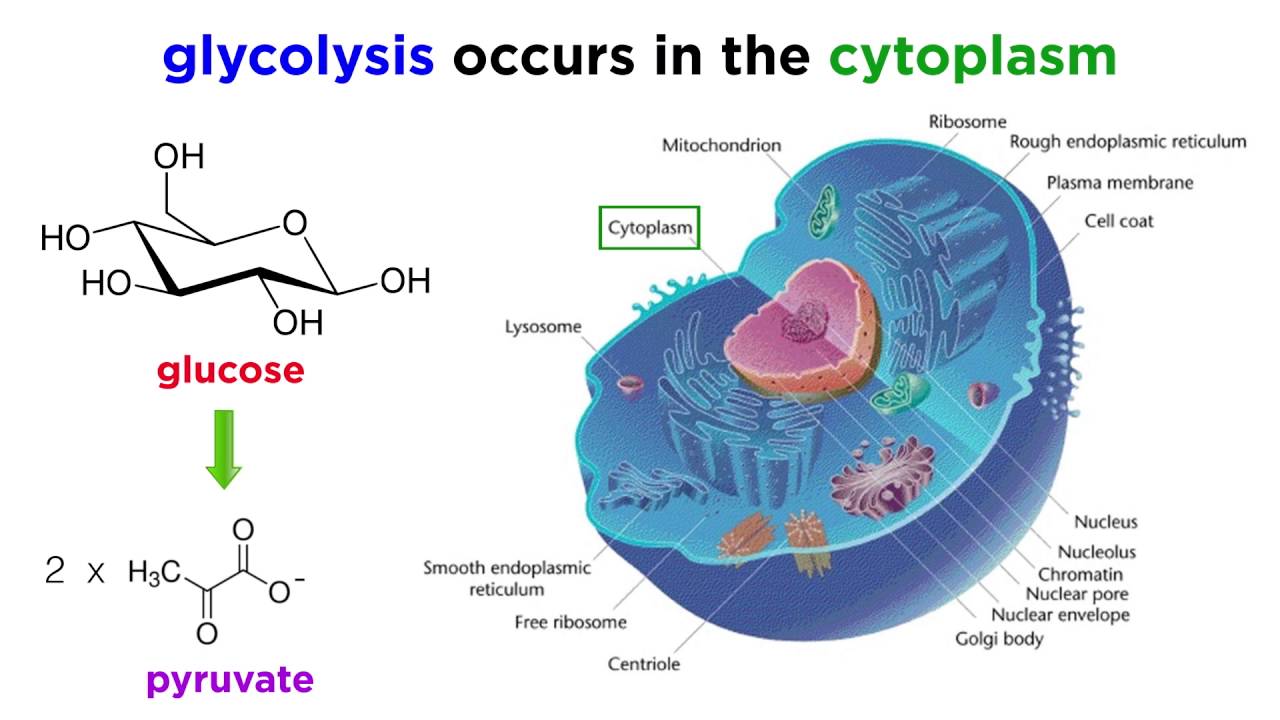
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Related Biology Terms. Cellular respiration refers to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often synonymous with aerobic respiration.
ATP for use in energy-requiring activities of the cell. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis.